Use MCMC to do benchmark analysis
Project description
benchmcmc — Benchmark analysis with MCMC
Install
Installing is as always
pip install benchmcmc
It depends on pymc3 and
matplotlib, so these are also
installed.
Quickstart
Getting started real quick:
benchmcmc --generate 69 11 10 131 10 9 --beta > bench.txt
benchmcmc bench.txt
Introduction
This package lets you take a series of benchmark data analyses whether there at one point was a change in performance.
Suppose that you run your benchmark tests on every commit that you have
(e.g. looping over git-rev-list),
and you see that your performance data
is (e.g. in requests per second or in seconds, or other measures)
as follows:
13.64
12.82
11.69
15.12
12.30
18.46
13.51
14.33
13.84
12.77
... (180 rows omitted)
10.93
11.02
12.45
11.78
12.12
13.51
10.66
10.18
10.81
12.19
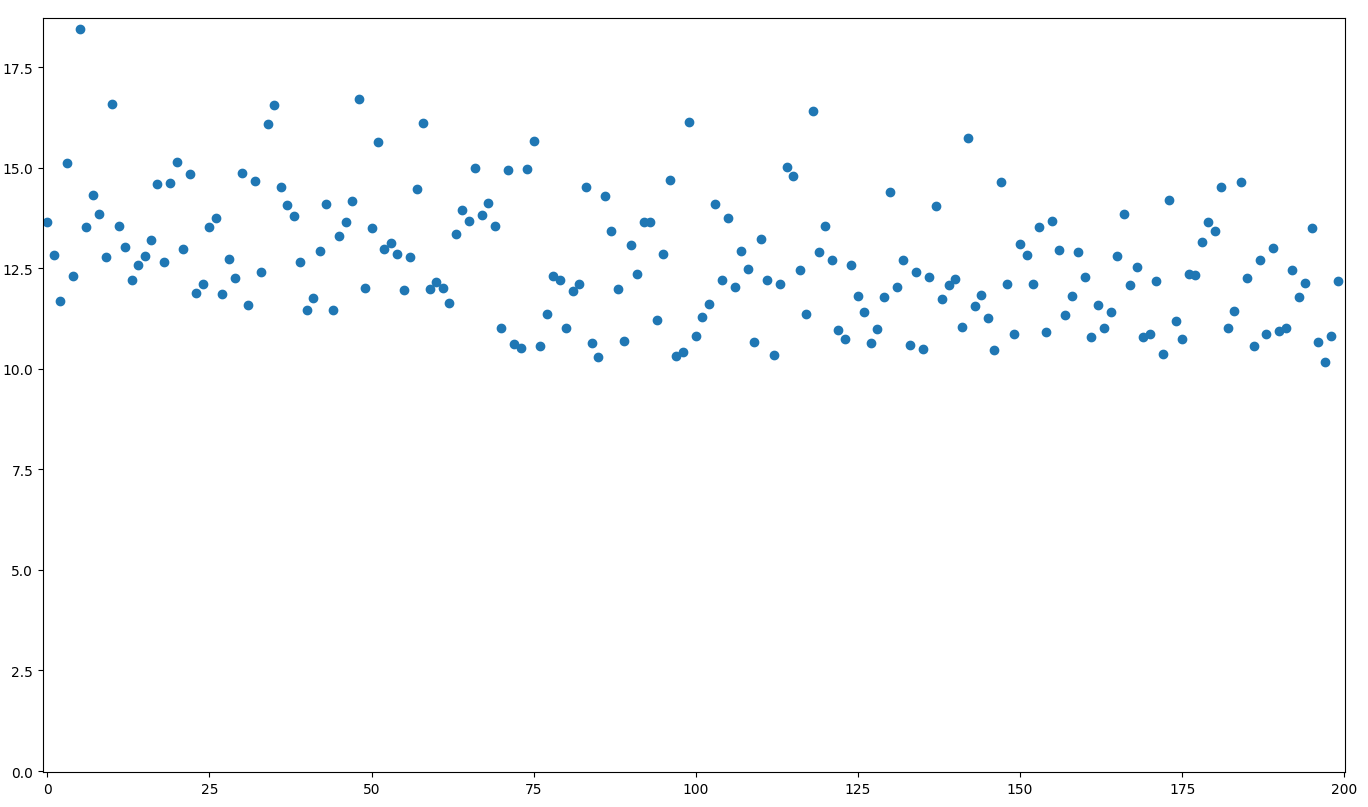
In this data, it seems to be centered around 13+ε in the beginning, and it ends being centered around 12+ε, or visualized:
There seems to be a slight drop in values before the 100th point, but it's not easy to determine exactly where the change occurred.
Suppose that you wonder whether or not the performance at the start and at the end are likely to be from two different distributions, and if so, where the switchpoint was.
Analysis
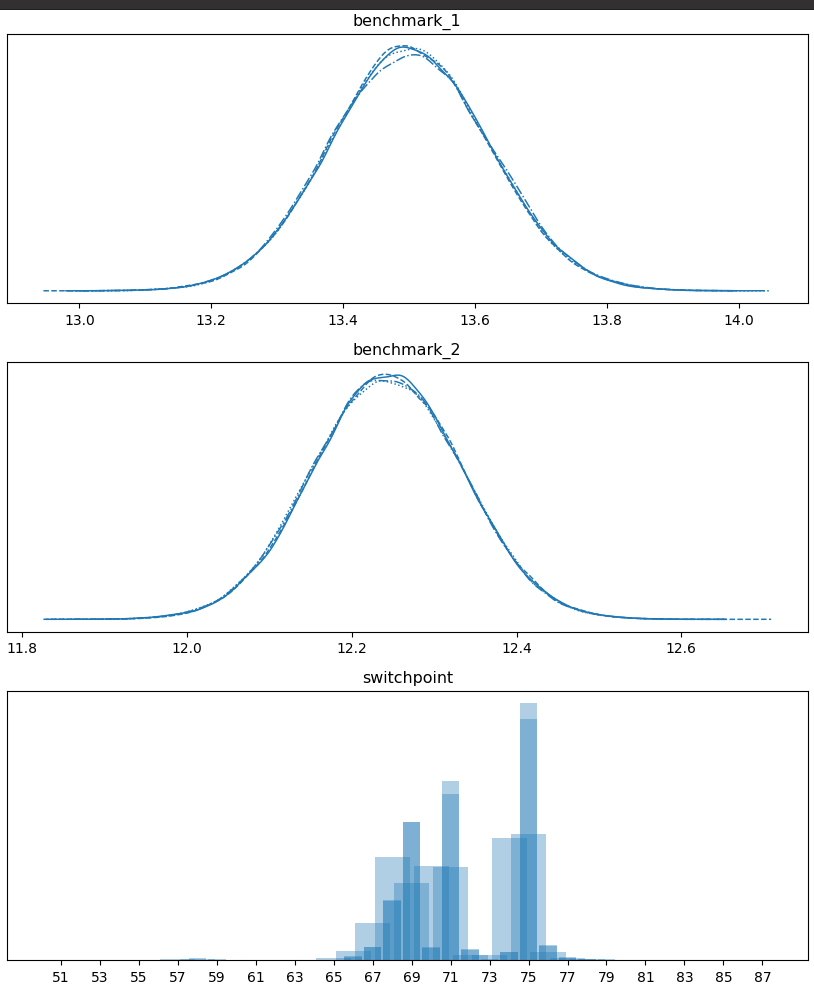
Running benchmcmc on the data gives the above plot which shows that it
is likely that the performance went from ~13.5 to ~12.25 at or around the
69th or 75th datapoints.
This helps you pin down when a performance change might have occurred.
Generating synthetic data
You can run benchmcmc --generate for generating synthetic benchmark
data.
$ benchmcmc --generate 100 15 3 100 14 3 [--beta] > benchmarkfile.txt
This generates 200 samples, 100 from N(mu=15, sigma=3) followed by 100
from N(mu=14, sigma=3).
If you use --beta, you get a bit more realistic performance with a
lower bound of mu, especially for lower values of mu.
Running a script on a history
Suppose that you want to run python script.py on a script that is in
your Git tree.
LOGFILE=/tmp/timescript
echo "" > $LOGFILE
for commit in $(git rev-list master)
do
git checkout $commit
printf "%s," "`(git rev-parse --short HEAD)`" >> $LOGFILE
/usr/bin/time -a -o $LOGFILE --format=%e python script.py
done
tac $LOGFILE
When run in a repository, it will output time data in the format
commit,time
Here is an example of the output:
484fde8,0.04
58a1cdb,0.04
d26b797,0.04
81f4b9a,0.04
3ae1e11,0.04
7689ca2,0.04
8c76b29,0.04
43db50c,0.04
b34b146,0.04
4c56a54,0.04
9c08050,0.07
b22278d,0.07
7a9c111,0.07
065b6a5,0.07
6cc7cdd,0.07
ec7f042,0.07
b3ba887,0.08
a32ce81,0.07
9136914,0.07
b456714,0.07
504cf73,0.07
8002774,0.07
e1f5f9f,0.09
Project details
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.