Complete set of Eve Universe models with on-demand loading from ESI
Project description
Eve Universe
Complete set of Eve Online Universe models in Django with on-demand loading from ESI






Contents
- Overview
- Installation
- Models
- Examples
- API
- Test data
- Settings
- Management commands
- Database tools
- Change Log
Overview
django-eveuniverse is a foundation app meant to help speed up the development of Django apps that are using data from ESI. It provides all Eve Universe classes as Django models, including all relationships between then, ready to be used in your project. Furthermore, all Eve models have an on-demand loading mechanism that allows you to load and store every eve objects ad-hoc.
Here is an overview of the main features:
- Complete set of Eve Universe objects as Django models like regions, types or planets.
- On-demand loading mechanism that allows retrieving Eve universe objects ad-hoc from ESI
- Management commands for preloading often used sets of data like the map or ships types
- Eve models come with additional useful features, e.g. a route finder between solar systems or image URLs for types
- Special model EveEntity for quickly resolving Eve Online IDs to names
- Optional asynchronous loading of eve models and loading of all related children. (e.g. load all types for a specific group)
Installation
Step 1 - Install app into your venv
pip install django-eveuniverse
Step 2 - Settings
Add eveuniverse to INSTALLED_APPS in your the settings file.
By default only the core models are automatically loaded on-demand. If you want to also include some of the additional models please add them to your settings.
Step 3 - Setup celery
This app uses celery for loading large sets of data, e.g. with the load commands. Please make sure celery is setup and working for your Django project.
Note on celery worker setup
For an efficient loading of large amounts of data from ESI we recommend a thread based setup of celery workers with at least 10 concurrent workers.
For example on our test system with 20 gevent threads the loading of the complete Eve Online map (with the command: eveuniverse_load_data map) consisting of all regions, constellation and solar systems took only about 5 minutes.
Step 4 - Run migrations
python manage.py migrate
Step 5 - Finalize installation
Finally restart your Django instance so your changes become effective.
Examples
Using the eve models in your own project is straightforward. The syntax is similar to the standard manager methods for Django modes.
Here is an example:
from eveuniverse.models import EveSolarSystem
# get the Jita solar system and load it ad-hoc if needed
jita, _ = EveSolarSystem.objects.get_or_create_esi(id=30000142)
# this will output True
print(jita.is_high_sec)
# this will output the name of it's constellation: Kimotoro
print(jita.eve_constellation.name)
Models
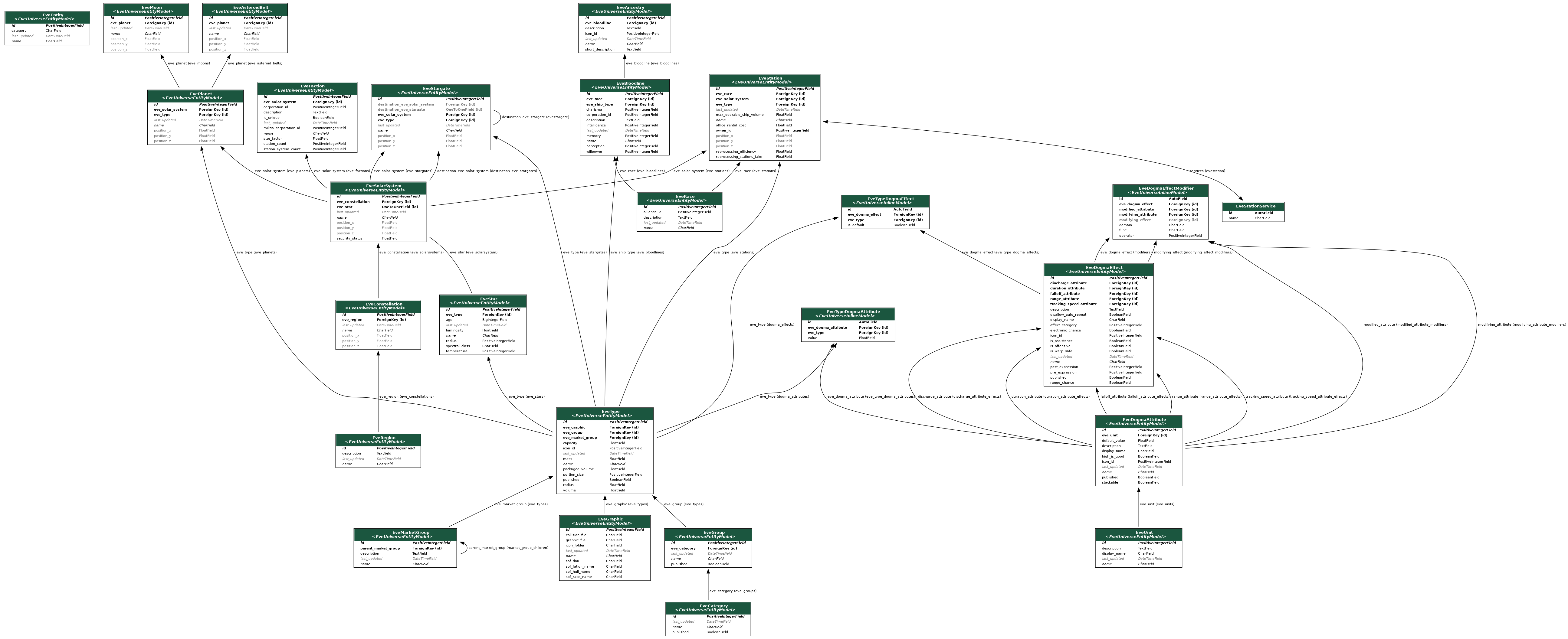
The following graph shows all models and how they are interrelated:
Here is a list of the main models, each representing and Eve object:
- EveAncestry
- EveAsteroidBelt
- EveBloodline
- EveCategory
- EveConstellation
- EveDogmaAttribute
- EveDogmaEffect
- EveEntity
- EveFaction
- EveGraphic
- EveGroup
- EveMarketGroup
- EveMoon
- EvePlanet
- EveRace
- EveRegion
- EveSolarSystem
- EveStar
- EveStargate
- EveStation
- EveType
- EveUnit
API
Every eve model has an id and name property and comes with a set of basic methods:
get_or_create_esi(id=12345678): gets or creates an Eve universe object. The object is automatically fetched from ESI if it does not exist (blocking). Will always get/create parent objects.update_or_create_esi(id=12345678): updates or creates an Eve universe object by fetching it from ESI (blocking). Will always get/create parent objects.
Please see each model for a list of additional methods and properties.
Test data
django-eveuniverse comes with tools that help you generate and use test data for your own apps.
Generate test data
To generate your testdata create a script within your projects and run that scrip as a Django test. That is important to ensure that the database on which the scripts operates is empty. That script will then create a JSON file that contains freshly retrieved Eve objects from ESI based on your specification.
create_eveuniverse.py
Here is an example script for generating test data (taken from aa-killtracker):
from django.test import TestCase
from eveuniverse.tools.testdata import create_testdata, ModelSpec
from . import test_data_filename
class CreateEveUniverseTestData(TestCase):
def test_create_testdata(self):
testdata_spec = {
"EveFaction": ModelSpec(ids=[500001], include_children=False),
"EveType": ModelSpec(
ids=[603, 621, 638, 2488, 2977, 3756, 11379, 16238, 34562, 37483],
include_children=False,
),
"EveSolarSystem": ModelSpec(
ids=[30001161, 30004976, 30004984, 30045349, 31000005],
include_children=False,
),
"EveRegion": ModelSpec(ids=[10000038], include_children=True,),
}
create_testdata(testdata_spec, test_data_filename())
Using generated testdata in your tests
To user the generated testdata file in your test you need another script that creates objects from your generated JSON file.
load_eveuniverse.py
Here is an example script that creates objects from the JSON file.
import json
from eveuniverse.tools.testdata import load_testdata_from_dict
from . import test_data_filename
def _load_eveuniverse_from_file():
with open(test_data_filename(), "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
data = json.load(f)
return data
eveuniverse_testdata = _load_eveuniverse_from_file()
def load_eveuniverse():
load_testdata_from_dict(eveuniverse_testdata)
You can then load all Eve objects in your own test script like so:
test_example.py
from django.test import TestCase
from .load_eveuniverse import load_eveuniverse
class MyTest(TestCase):
@classmethod
def setUpClass(cls):
super().setUpClass()
load_eveuniverse()
def test_my_test(self):
svipul = EveType.objects.get(id=34562)
# ...
Settings
Here is a list of available settings for this app. They can be configured by adding them to your local Django settings file.
Most settings will enable the automatic loading of related models. Note that this will exponentially increase load times of objects, so we recommend to only enable additional models that are functionally needed. For example: if you enable Planets, all related planet object are automatically loaded when updating a solar system.
| Name | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
EVEUNIVERSE_LOAD_ASTEROID_BELTS |
When true will automatically load astroid belts with every planet | False |
EVEUNIVERSE_LOAD_DOGMAS |
when true will automatically load dogma, e.g. with every type | False |
EVEUNIVERSE_LOAD_GRAPHICS |
when true will automatically load graphics with every type | False |
EVEUNIVERSE_LOAD_MARKET_GROUPS |
when true will automatically load market groups with every type | False |
EVEUNIVERSE_LOAD_MOONS |
when true will automatically load moons be with every planet | False |
EVEUNIVERSE_LOAD_PLANETS |
when true will automatically load planets with every solar system | False |
EVEUNIVERSE_LOAD_STARGATES |
when true will automatically load stargates with every solar system | False |
EVEUNIVERSE_LOAD_STARS |
when true will automatically load stars with every solar system | False |
EVEUNIVERSE_LOAD_STATIONS |
when true will automatically load stations be with every solar system | False |
Note that all settings are optional and the app will use the documented default settings if they are not used.
Management commands
The following management commands are available:
- eveuniverse_load_data: This command will load a complete set of data form ESI and store it locally. Useful to optimize performance or when you want to provide the user with drop-down lists. Available sets:
- map: All regions, constellations and solar systems
- ships: All ship types
- structures: All structures types
- structures_purge_all: This command will purge ALL data of your models.
Database tools
On some DBMSs like MySQL it is not possible to reset the database and remove all eveuniverse tables with the standard "migrate zero" command. The reason is that eveuniverse is using composite primary keys and Django seams to have problems dealing with that correctly, when trying to roll back migrations.
As workaround you will need remove all tables with SQL commands. To make this easier we are providing a SQL script that contains all commands to drop the tables. The full process for "migrating to zero" is as follows:
- Run SQL script
drop_tables.sqlon your database - Run
python manage.py migrate eveuniverse zero --fake
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.