Easy async ORM for python, built with relations in mind
Project description





Introduction
Tortoise ORM is an easy-to-use asyncio ORM (Object Relational Mapper) inspired by Django.
You can find the docs at Documentation
Tortoise ORM supports CPython 3.10 and later for SQLite, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, and Oracle.
Why was Tortoise ORM built?
Tortoise ORM was built to provide a lightweight, async-native Object-Relational Mapper for Python with a familiar Django-like API.
Tortoise ORM performs well when compared to other Python ORMs. Here are our benchmarks on PostgreSQL 17, where we measure different read and write operations (rows/sec, more is better):
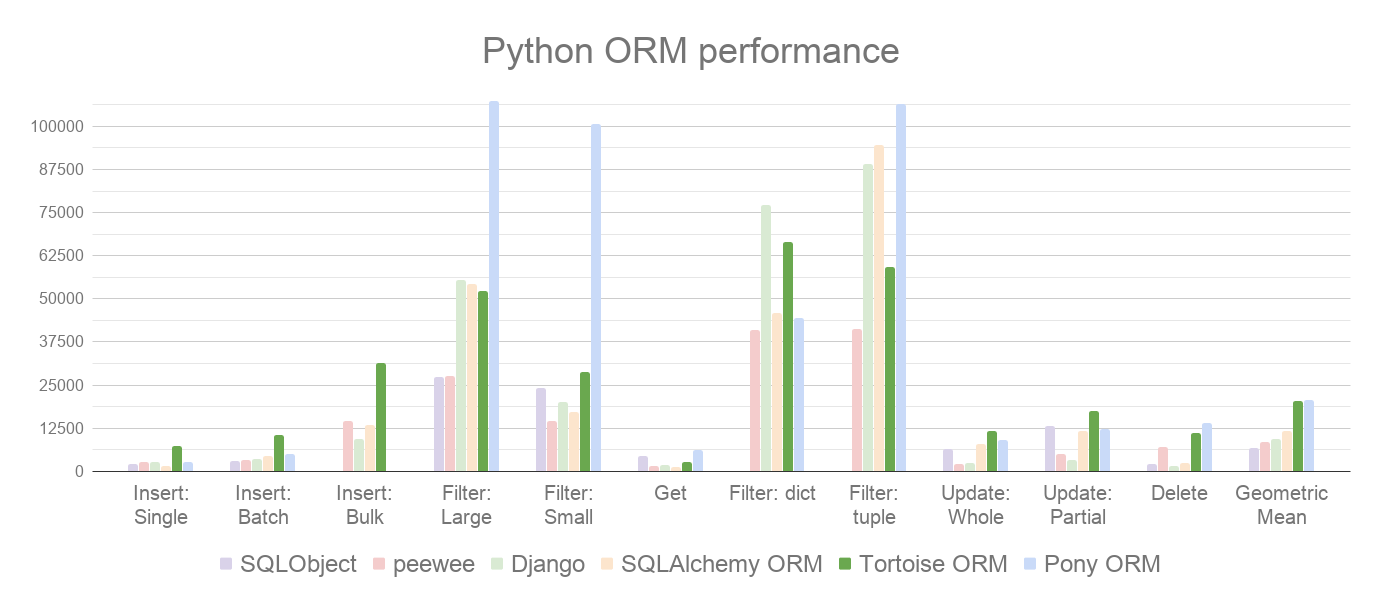
How is an ORM useful?
An Object-Relational Mapper (ORM) abstracts database interactions, allowing developers to work with databases using high-level, object-oriented code instead of raw SQL.
Reduces boilerplate SQL, allowing faster development with cleaner, more readable code.
Helps prevent SQL injection by using parameterized queries.
Centralized schema and relationship definitions make code easier to manage and modify.
Handles schema changes through version-controlled migrations.
Getting Started
Installation
The following table shows the available installation options for different databases (note that there are multiple options of clients for some databases):
Database |
Installation Command |
|---|---|
SQLite |
pip install tortoise-orm |
PostgreSQL (psycopg) |
pip install tortoise-orm[psycopg] |
PostgreSQL (asyncpg) |
pip install tortoise-orm[asyncpg] |
MySQL (aiomysql) |
pip install tortoise-orm[aiomysql] |
MySQL (asyncmy) |
pip install tortoise-orm[asyncmy] |
MS SQL |
pip install tortoise-orm[asyncodbc] |
Oracle |
pip install tortoise-orm[asyncodbc] |
Quick Tutorial
Define the models by inheriting from tortoise.models.Model.
from tortoise.models import Model
from tortoise import fields
class Tournament(Model):
id = fields.IntField(primary_key=True)
name = fields.CharField(max_length=20)
class Event(Model):
id = fields.BigIntField(primary_key=True)
name = fields.TextField()
tournament = fields.ForeignKeyField('models.Tournament', related_name='events', on_delete=fields.OnDelete.CASCADE)
participants = fields.ManyToManyField('models.Team', related_name='events', through='event_team', on_delete=fields.OnDelete.SET_NULL)
class Team(Model):
id = fields.UUIDField(primary_key=True)
name = fields.CharField(max_length=20, unique=True)After defining the models, Tortoise ORM needs to be initialized to establish the relationships between models and connect to the database. The code below creates a connection to a SQLite DB database with the aiosqlite client. generate_schema sets up schema on an empty database. generate_schema is for development purposes only; use the built-in migrations for production use.
from tortoise import Tortoise, run_async
async def init():
# Here we connect to a SQLite DB file.
# also specify the app name of "models"
# which contain models from "app.models"
await Tortoise.init(
db_url='sqlite://db.sqlite3',
modules={'models': ['app.models']}
)
# Generate the schema
await Tortoise.generate_schemas()
run_async(main())run_async is a helper function to run simple Tortoise scripts. Check out Documentation for FastAPI, Sanic and other integrations.
With the Tortoise initialized, the models are available for use:
async def main():
await Tortoise.init(
db_url='sqlite://db.sqlite3',
modules={'models': ['app.models']}
)
await Tortoise.generate_schemas()
# Creating an instance with .save()
tournament = Tournament(name='New Tournament')
await tournament.save()
# Or with .create()
await Event.create(name='Without participants', tournament=tournament)
event = await Event.create(name='Test', tournament=tournament)
participants = []
for i in range(2):
team = await Team.create(name='Team {}'.format(i + 1))
participants.append(team)
# One to Many (ForeignKey) relations support creating related objects
another_event = await tournament.events.create(name='Another Event')
# Many to Many Relationship management is quite straightforward
# (there are .remove(...) and .clear() too)
await event.participants.add(*participants)
# Iterate over related entities with the async context manager
async for team in event.participants:
print(team.name)
# The related entities are cached and can be iterated in the synchronous way afterwards
for team in event.participants:
pass
# Use prefetch_related to fetch related objects
selected_events = await Event.filter(
participants=participants[0].id
).prefetch_related('participants', 'tournament')
for event in selected_events:
print(event.tournament.name)
print([t.name for t in event.participants])
# Prefetch multiple levels of related entities
await Team.all().prefetch_related('events__tournament')
# Filter and order by related models too
await Tournament.filter(
events__name__in=['Test', 'Prod']
).order_by('-events__participants__name').distinct()
run_async(main())Learn more at the documentation site
Migrations
Tortoise ORM ships with a built-in migration framework and CLI. Autodetect model changes, generate migration files, and apply them:
tortoise init # create migration packages
tortoise makemigrations # detect changes and generate migrations
tortoise migrate # apply pending migrations
tortoise sqlmigrate app 001 # preview SQL without executingMigrations support RunPython and RunSQL for data migrations, offline migration generation, reversible operations, and multi-app and multi db-schema projects.
See the migrations documentation for full setup and examples.
Contributing
Please have a look at the Contribution Guide.
License
This project is licensed under the Apache License - see the LICENSE.txt file for details.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file tortoise_orm-1.0.0.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: tortoise_orm-1.0.0.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 343.0 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.13.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
d66188f70c74fd7ea24f294f42f0b16ba9a2b6cdd95d0fcb2fb6cb41759947f4
|
|
| MD5 |
f5e604467ead3018bc30dd7ba4fd18f8
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
8dacd36638e5fc6d3f98ae5dd4d2aba46bc9510add63cd6c643a58db85b0d55e
|
File details
Details for the file tortoise_orm-1.0.0-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: tortoise_orm-1.0.0-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 252.7 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.13.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
4f5b609f6e41914a64c9a80233fc5d2e612e7eb1c7b880627d67cd0710ee9bb5
|
|
| MD5 |
15b6b66614e35146494e7793696900cf
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
71eaa87942eda8d506b5130cfc33ddd6bc3b937c2e505cfb4e5c91ede2768b5b
|













